

COGS does not include indirect expenses, like certain overhead costs. Businesses thus try to keep their COGS low so that net profits will be higher.Īnd when you know your business’s gross profit, you can calculate your net income or profit, which is the amount your business earns after subtracting all expenses.
While this movement is beneficial for income tax purposes, the business will have less profit for its shareholders.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Sampleincomestatement-d92415c1850943f99cad74a3cb3bbf20.jpg)
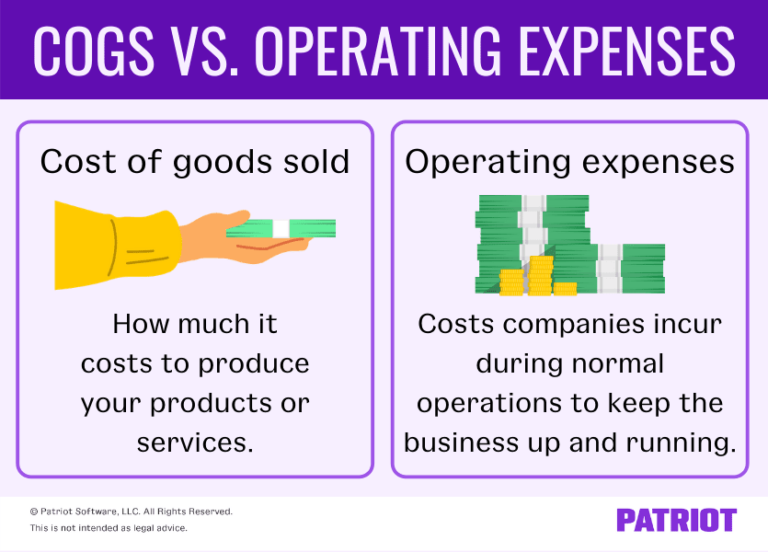
Knowing the cost of goods sold helps analysts, investors, and managers estimate the company’s bottom line. Because COGS is a cost of doing business, it is recorded as a business expense on the income statements. The cost of sending the cars to dealerships and the cost of the labor used to sell the car would be excluded. Consequently, their values are recorded as different line items on a company’s income statement. Operating expenses (OPEX) and cost of goods sold (COGS) are separate sets of expenditures incurred by businesses in running their daily operations. Operating expenses (OPEX) and cost of goods sold (COGS) are discrete expenditures incurred by businesses. Even though we do not see the word Expense this in fact is an expense item found on the Income Statement as a reduction to Revenue. Cost of Goods Sold is an EXPENSE item with a normal debit balance (debit to increase and credit to decrease). Cost of goods sold is the inventory cost to the seller of the goods sold to customers. Thus, they mistakenly assume items that have been stolen have been sold and include their cost in cost of goods sold. The costs of those goods which are not yet sold are deferred as costs of inventory until the inventory is sold or written down in value. Costs of goods made by the businesses include material, labor, and allocated overhead. Additional costs may include freight paid to acquire the goods, customs duties, sales or use taxes not recoverable paid on materials used, and fees paid for acquisition.Ĭosts include all costs of purchase, costs of conversion and other costs that are incurred in bringing the inventories to their present location and condition. Bookkeeping by Adam Hill Accounting Principles IIīut both of these expenses are subtracted from the company’s total sales or revenue figures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
